【完全版】スムーススクロールの実装は全てこれでいい【LazyLoad対応】
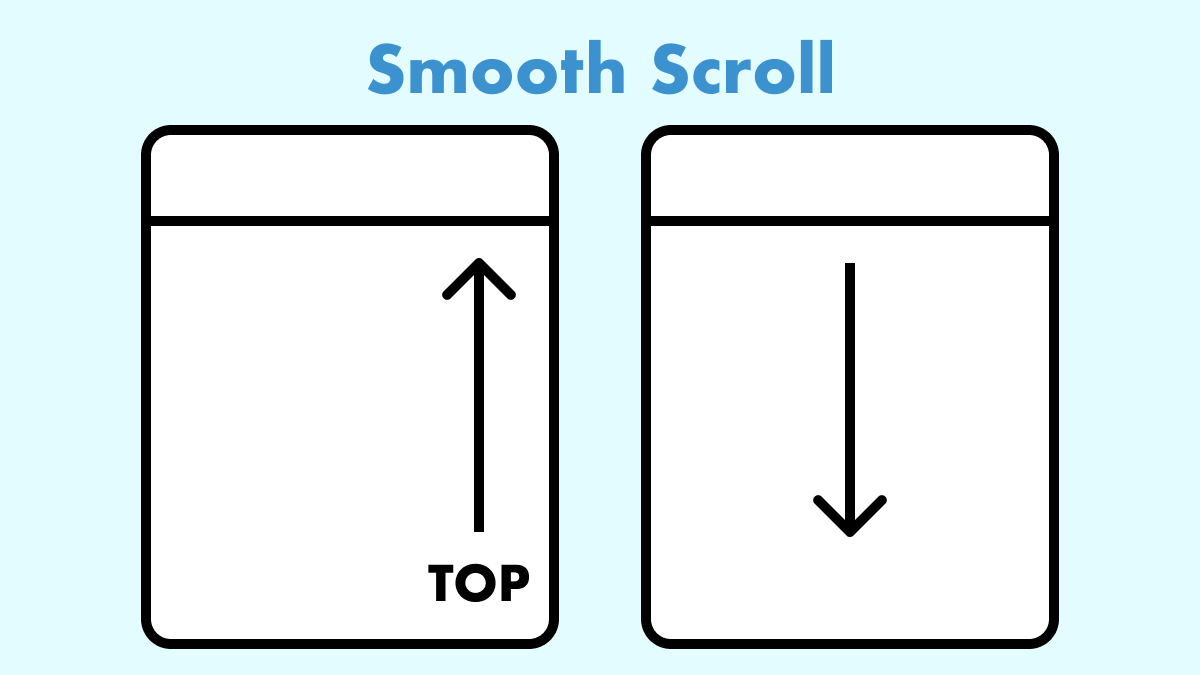
コードを見直し細かい箇所をリファクタリングしました。主要ブラウザ全てで動作確認済みです。
JavaScriptを使った、実用的なスムーススクロールの実装方法を詳しくご紹介します。
固定ヘッダーによる重なりや、遅延読み込みによる位置ずれへの対策も含まれているので、これ一つで多くのケースに対応可能です。
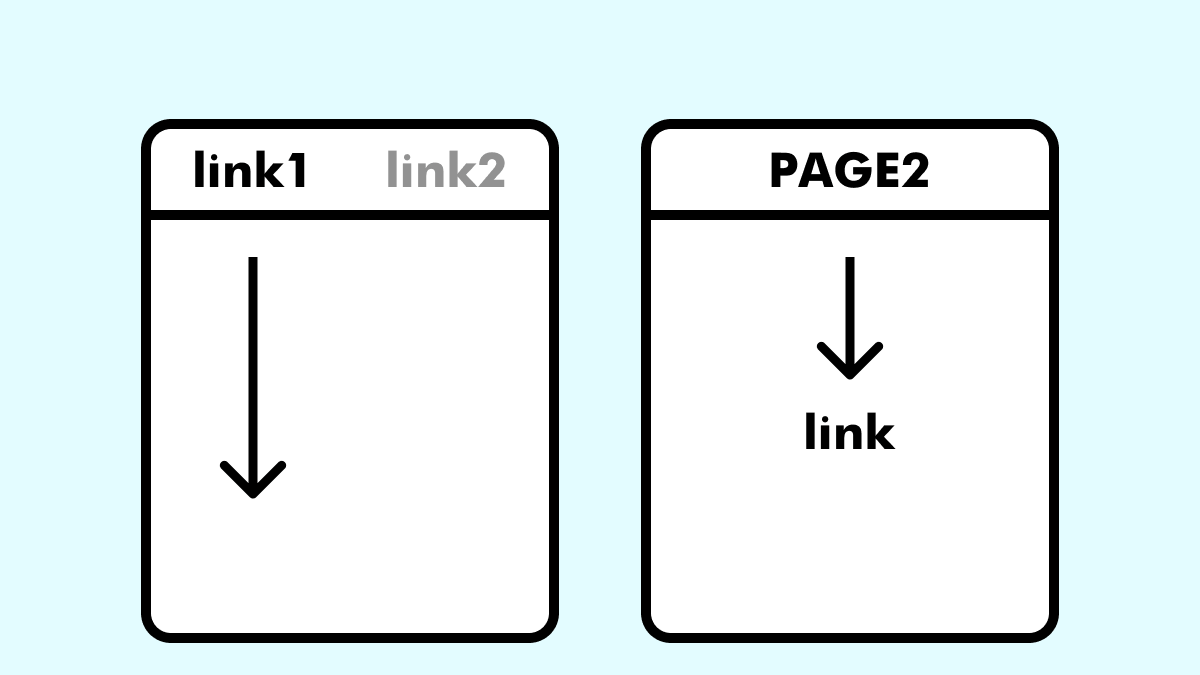
もちろん、ページ内リンクだけでなく、別ページから遷移した際のスクロールにも対応しています。
滑らかな操作感を重視し、イージングには「easeOutExpo」を採用しました。
ベースとなるコード
カスタマイズ前の標準的なスムーススクロールのコードです。(シンプルに実装したい場合はこちらでもOK)
// ヘッダー情報
const header = document.querySelector(".fixed-header");
const headerHeight = header ? header.offsetHeight + 20 : 0;
// ページ内のスムーススクロール
for (const link of document.querySelectorAll('a[href*="#"]')) {
link.addEventListener('click', (e) => {
const hash = e.currentTarget.hash;
const target = document.getElementById(hash.slice(1));
// ページトップへ("#"と"#top")
if (!hash || hash === '#top') {
e.preventDefault();
window.scrollTo({
top: 0,
behavior: 'smooth',
});
// アンカーへ
} else if (target) {
e.preventDefault();
const position = target.getBoundingClientRect().top + window.scrollY - headerHeight;
window.scrollTo({
top: position,
behavior: "smooth",
});
// URLにハッシュを含める
history.pushState(null, '', hash);
}
});
};
// 別ページ遷移後にスムーススクロール
const urlHash = window.location.hash;
if (urlHash) {
const target = document.getElementById(urlHash.slice(1));
if (target) {
// ページトップから開始(ブラウザ差異を考慮して併用)
history.replaceState(null, '', window.location.pathname);
window.scrollTo(0, 0);
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
const position = target.getBoundingClientRect().top + window.scrollY - headerHeight;
window.scrollTo({
top: position,
behavior: "smooth",
});
// ハッシュを再設定
history.replaceState(null, '', window.location.pathname + urlHash);
});
}
}jQuery版はこちら
完全版スムーススクロールのコード
こちらは、イージングの追加と遅延読み込みによる位置ずれを対策したものです。
// ヘッダー情報
const header = document.querySelector(".fixed-header");
const headerHeight = header ? header.offsetHeight + 20 : 0;
// イージング関数(easeOutExpo)
function scrollToPos(position) {
const startPos = window.scrollY;
const distance = Math.min(
position - startPos,
document.documentElement.scrollHeight - window.innerHeight - startPos
);
const duration = 800; // スクロールにかかる時間(ミリ秒)
let startTime;
function easeOutExpo(t, b, c, d) {
return (c * (-Math.pow(2, (-10 * t) / d) + 1) * 1024) / 1023 + b;
}
function animation(currentTime) {
if (startTime === undefined) {
startTime = currentTime;
}
const timeElapsed = currentTime - startTime;
const scrollPos = easeOutExpo(timeElapsed, startPos, distance, duration);
window.scrollTo(0, scrollPos);
if (timeElapsed < duration) {
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
} else {
window.scrollTo(0, position);
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
}
// 画像の強制読み込み
function loadImages() {
const targets = document.querySelectorAll("[data-src]");
for (const target of targets) {
const dataSrc = target.getAttribute("data-src");
const currentSrc = target.getAttribute("src");
// data-src と src が異なる場合のみコピーする
if (dataSrc !== currentSrc) {
target.setAttribute("src", dataSrc);
}
}
}
// ページ内のスムーススクロール
for (const link of document.querySelectorAll('a[href*="#"]')) {
link.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
const hash = e.currentTarget.hash;
const target = document.getElementById(hash.slice(1));
// ページトップへ("#"と"#top")
if (!hash || hash === "#top") {
e.preventDefault();
scrollToPos(0);
// アンカーへ
} else if (target) {
e.preventDefault();
loadImages();
const position =
target.getBoundingClientRect().top + window.scrollY - headerHeight;
scrollToPos(position);
// URLにハッシュを含める
history.pushState(null, "", hash);
}
});
}
// 別ページ遷移後のスムーススクロール
const urlHash = window.location.hash;
if (urlHash) {
const target = document.getElementById(urlHash.slice(1));
if (target) {
// ページトップから開始(ブラウザ差異を考慮して併用)
history.replaceState(null, "", window.location.pathname);
window.scrollTo(0, 0);
loadImages();
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
const position =
target.getBoundingClientRect().top + window.scrollY - headerHeight;
scrollToPos(position);
// ハッシュを再設定
history.replaceState(null, "", window.location.pathname + urlHash);
});
}
}こちらを実装したデモサイトの「フッターメニュー」で動きを確認できます。
- ユーザー名:demo
- パスワード:demo
ヘッダー情報の解説
// ヘッダー情報
const header = document.querySelector(".fixed-header");
const headerHeight = header ? header.offsetHeight + 20 : 0;ヘッダーを固定させる場合は、ヘッダー要素にfixed-headerクラスを追加します。
このクラスがある場合は「ヘッダーの高さ+20px(任意のオフセット)」を代入、クラスがなければ「0」を代入して計算されます。
イージング関数の解説
// イージング関数(easeOutExpo)
function scrollToPos(position) {
const startPos = window.scrollY;
const distance = Math.min(position - startPos, document.documentElement.scrollHeight - window.innerHeight - startPos);
const duration = 800; // スクロールにかかる時間(ミリ秒)
let startTime;
function easeOutExpo(t, b, c, d) {
return c * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * t / d) + 1) * 1024 / 1023 + b;
}
function animation(currentTime) {
if (startTime === undefined) {
startTime = currentTime;
}
const timeElapsed = currentTime - startTime;
const scrollPos = easeOutExpo(timeElapsed, startPos, distance, duration);
window.scrollTo(0, scrollPos);
if (timeElapsed < duration) {
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
} else {
window.scrollTo(0, position);
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
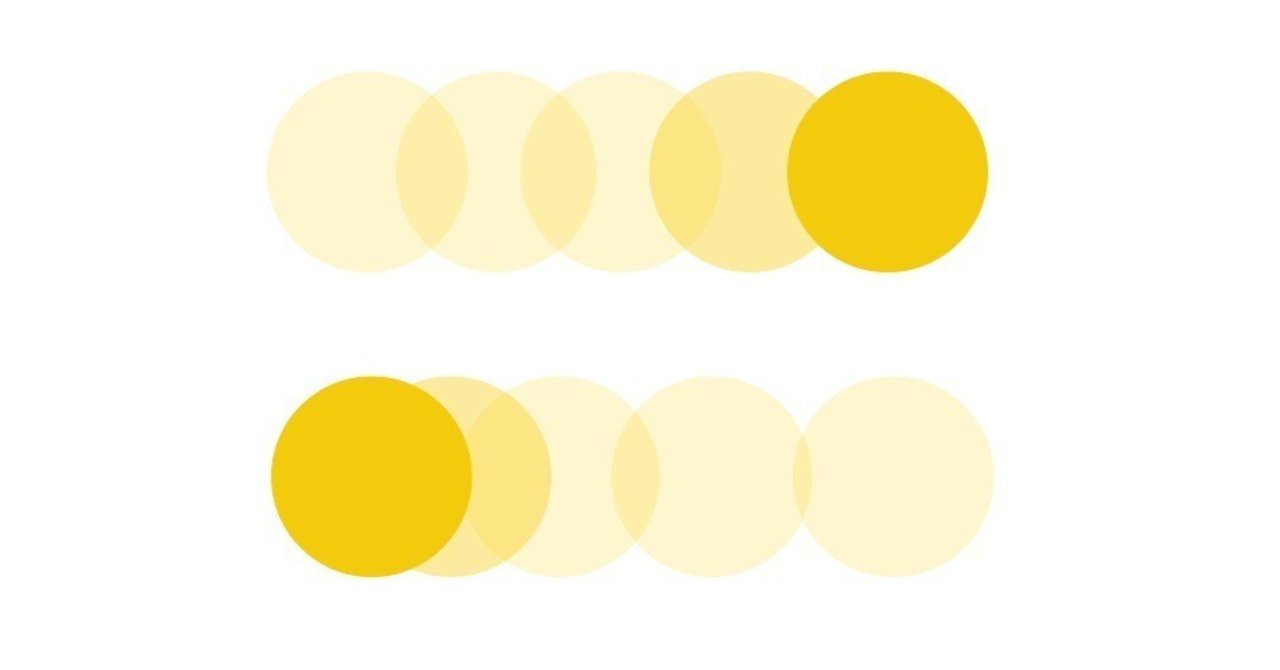
}イージングには、徐々に減速する動きが最も強いイーズアウト「easeOutExpo」を採用しました。
これは、指で弾いた瞬間が最も速く、摩擦で徐々に減速するといった物理法則を再現しており、スムーススクロールに最適です。
このメリハリのある動きにより、自己帰属感(操作の感覚)が向上します。
参考にした記事
イージングを変更したい場合は、ChatGPTに頼るなどして、以下の2箇編集する必要があります。
function easeOutExpo(t, b, c, d) {
return c * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * t / d) + 1) * 1024 / 1023 + b;
}
↓
function easeOutQuart(t, b, c, d) {
return -c * ((t = t / d - 1) * t * t * t - 1) + b;
}
const scrollPos = easeOutExpo( // ...
↓
const scrollPos = easeOutQuart( // ...スクロールの最大距離を制限
const distance = Math.min(position - startPos, document.documentElement.scrollHeight - window.innerHeight - startPos);スクロール先のターゲットが画面の高さより小さい場合、最終地点まで滑らかなアニメーションが行われなくなることがあります。
どういった状況かというと、以下のサンプルでfooterをクリックしたときのぶつかるような動作です。
See the Pen ページ下部のセクションが低い場合のスクロール挙動 by hisa (@hisaaashi) on CodePen.
これは、ページの長さが足りないため、footer要素がヘッダー付近までスクロールすることができず、強制的にストップされているという状況です。
その対策として、min()関数を使い「ターゲットまでの距離」と「ページの残りの距離」の小さい方を最大距離とすることで解決しました。
誤差によるズレを修正
if (timeElapsed < duration) {
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
} else {
window.scrollTo(0, position); // スクロール位置がずれないように修正
}イージングの計算式の誤差で、スクロール中に数ピクセルのズレが生じてしまう場合があるため、最終位置に到達させるための再スクロール処理を追加しています。
イージング関数の使い方
デフォルトでよく使われているコードを、以下のように置き換えることでイージングを使用することができます。
// 通常のスクロール
window.scrollTo({
top: position,
behavior: "smooth",
});
↓
// イージングによるスクロール
scrollToPos(position);画像の強制読み込みの解説
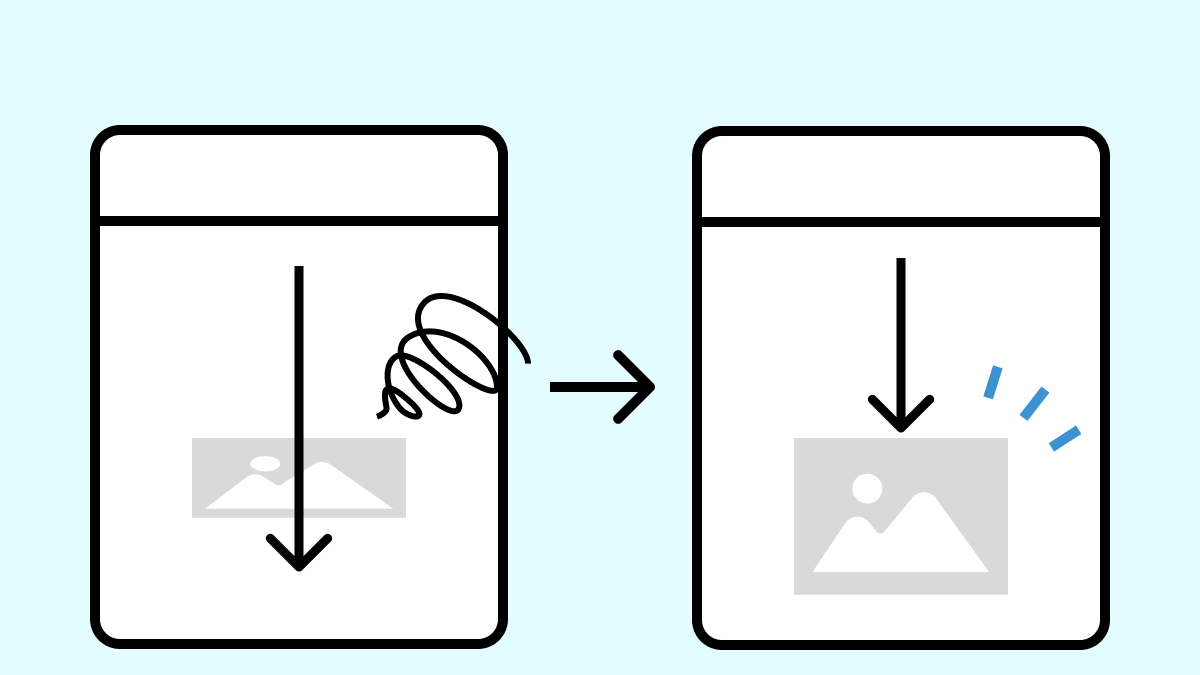
このコードは、JavaScriptライブラリによって遅延を行っている場合に有効です。
以下のコードは、data-src属性に格納されている画像のURLをsrc属性にコピーして、ダミー画像から本来の画像に置き換えるシンプルな処理です。
// 画像の強制読み込み
function loadImages() {
// data-srcを変数に格納
const targets = document.querySelectorAll("[data-src]");
// 全てのdata-srcを取得
for (const target of targets) {
const dataSrc = target.getAttribute("data-src");
const currentSrc = target.getAttribute("src");
// data-src と src が異なる場合のみコピーする
if (dataSrc !== currentSrc) {
target.setAttribute("src", dataSrc);
}
}
}
// 実行するタイミングで以下を記述
loadImages();この関数をスクロールする前に実行すれば、画像が読み込まれ正しい位置の計算できるという理屈です。
使用するライブラリによっては属性がdata-srcではない場合もあるので、属性名をライブラリの仕様に合わせて変更するか、以下の記事を参考にカスタマイズしてください。
ページ内のスムーススクロールの解説
// ページ内のスムーススクロール
for (const link of document.querySelectorAll('a[href*="#"]')) {
// ハッシュを含むaタグをクリックした時の処理
link.addEventListener('click', (e) => {
// ハッシュを取得
const hash = e.currentTarget.hash;
// スクロール先を取得
const target = document.getElementById(hash.slice(1));
// ページトップへ("#"と"#top")
if (!hash || hash === '#top') {
// デフォルトの動作をキャンセル
e.preventDefault();
// スクロール開始
scrollToPos(0);
// アンカーへ
} else if (target) {
// デフォルトの動作をキャンセル
e.preventDefault();
// 画像の強制読み込み
loadImages();
// スクロール先の位置を計算(ヘッダーの高さを引く)
const position = target.getBoundingClientRect().top + window.scrollY - headerHeight;
// スクロール実行
scrollToPos(position);
// URLにハッシュを含める
history.pushState(null, '', hash);
}
});
};コメント通りなので、割愛。
別ページ遷移後のスムーススクロールの解説
// 別ページ遷移後のスムーススクロール
// ハッシュを取得
const urlHash = window.location.hash;
// ハッシュが存在する時
if (urlHash) {
// スクロール先を取得
const target = document.getElementById(urlHash.slice(1));
// スクロール先が存在する時
if (target) {
// ページトップから開始(ブラウザ差異を考慮して併用)
history.replaceState(null, '', window.location.pathname); // ハッシュを削除
window.scrollTo(0, 0); // ページトップへジャンプ
// 画像の強制読み込み
loadImages();
// ページを読み込んで処理
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
// スクロール先の位置を計算(ヘッダーの高さを引く)
const position = target.getBoundingClientRect().top + window.scrollY - headerHeight;
// スクロール実行
scrollToPos(position);
// ハッシュを再設定
history.replaceState(null, '', window.location.pathname + urlHash);
});
}
}このコードの中でのポイントは、ページトップからスクロールさせるための処理です。
// ページトップから開始(ブラウザ差異を考慮して併用)
history.replaceState(null, '', window.location.pathname); // ハッシュを削除
window.scrollTo(0, 0); // ページトップへジャンプ- URLのハッシュ(#以下の部分)を削除して、アンカーリンクが自動で動作するのを防ぐ。
- ページの一番上に強制的にスクロールさせる。
ブラウザによってどちらかが効かず挙動が異なるため、2種類のアプローチを併用しました。
ページトップからのスクロールが不要な場合は、このコードを削除してください。
まとめ:実装は全部入りで解決
以上、完全版スムーススクロールのコードのご紹介でした。
イージングや秒数など好みがあるかと思いますので、必要に応じてカスタマイズしてください。
カスタマイズに困ったらお気軽にご相談を!
- 「ちょっとしたCSSの調整だけお願いしたい」
- 「不具合を直してほしい」
料金は3,000円〜、お支払いは銀行振込・Amazonギフトカードなど柔軟に対応してます🤔
お気軽にコメントどうぞ